Excel 2003 -
Enter, Edit, and Delete Data

Excel 2003
Enter, Edit, and Delete Data


/en/excel2003/create-open-and-save-workbooks/content/
You can enter three types of data in a cell: text, numbers, and formulas. Text is any entry that is not a number or formula. Numbers are values that are used when making calculations. Formulas are mathematical calculations.
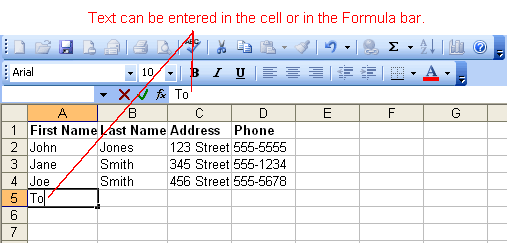
 to end the entry and turn off the Formula bar buttons.
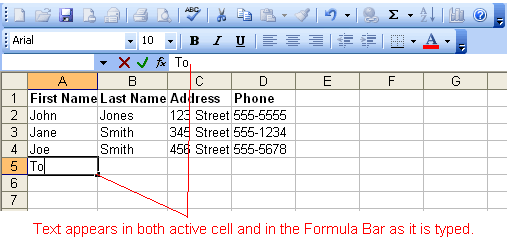
to end the entry and turn off the Formula bar buttons. Excel's AutoComplete feature keeps track of previously entered text. If the first few characters you type in a cell match an existing entry in that column, Excel fills in the remaining characters for you.
Excel's AutoComplete feature keeps track of previously entered text. If the first few characters you type in a cell match an existing entry in that column, Excel fills in the remaining characters for you.
Information in a spreadsheet is likely to change over time. Information can be changed in the following ways.
If the original entry is long and requires only a minor adjustment (in spelling, for example), then you can directly edit the information in the cell.
Method 1: Direct cell editing

 to complete the entry.
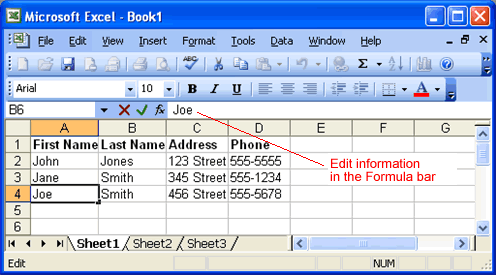
to complete the entry.Method 2: Formula bar editing
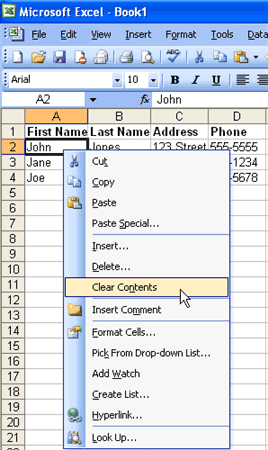
Sometimes you might do something to a spreadsheet that you didn't mean to do, like type the wrong number in a cell. Excel 2003 allows you to undo an operation. Use the  Undo button on the Standard toolbar to recover an error. The last single action is recoverable.
Undo button on the Standard toolbar to recover an error. The last single action is recoverable.
 Undo button.
Undo button.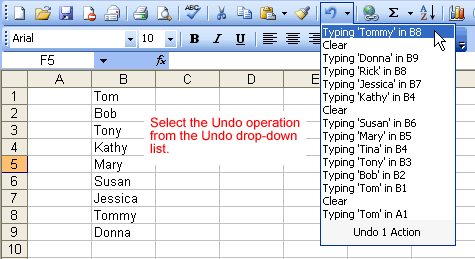
An Undo operation can be cancelled by applying a Redo. This is useful when an Undo operation was mistakenly applied. Remember, a Redo is possible only if you have not changed an Excel spreadsheet since the last Undo operation was completed:
 Redo button.
Redo button.The currently selected cell in Excel is called the active cell. You can also select a group of adjacent cells, or a cell range. Many operations can be performed against a cell range, including moving, copying, deleting, and formatting. A cell range can be defined in different ways: Select a specific range of cells, select multiple columns or rows, or select the entire worksheet.
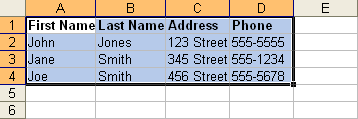
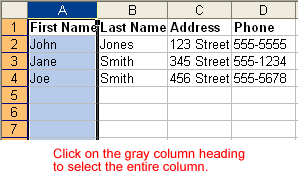
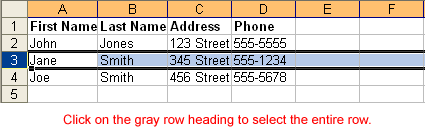
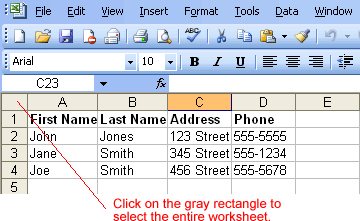
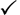 If the cells and columns you want to select are not directly next to one another, select one of the ranges you want to select and hold down the Control key while selecting other ranges.
If the cells and columns you want to select are not directly next to one another, select one of the ranges you want to select and hold down the Control key while selecting other ranges.
/en/excel2003/moving-copying-and-deleting-cell-contents/content/