Excel 2007 -
Working with Charts

Excel 2007
Working with Charts


/en/excel2007/using-whatif-analysis/content/
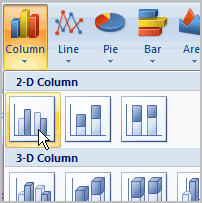 A chart is a tool you can use in Excel to communicate your data graphically. Charts allow your audience to more easily see the meaning behind the numbers in the spreadsheet, and to make showing comparisons and trends much easier. In this lesson, you will learn how to insert and modify Excel charts and see how they can be an effective tool for communicating information.
A chart is a tool you can use in Excel to communicate your data graphically. Charts allow your audience to more easily see the meaning behind the numbers in the spreadsheet, and to make showing comparisons and trends much easier. In this lesson, you will learn how to insert and modify Excel charts and see how they can be an effective tool for communicating information.
Download the example to work along with the video.
Charts can be a useful way to communicate data. When you insert a chart in Excel, it appears in the selected worksheet with the source data by default.
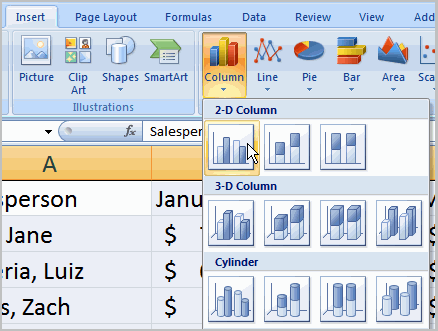
Have you ever read something you didn't fully understand but when you saw a chart or graph, the concept became clear and understandable? Charts are a visual representation of data in a worksheet. Charts make it easy to see comparisons, patterns, and trends in the data.
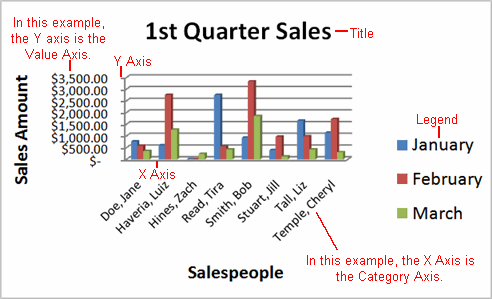
The range of cells that make up a chart. The chart is updated automatically whenever the information in these cells changes.
The title of the chart.
The chart key, which identifies what each color on the chart represents.
The vertical and horizontal parts of a chart. The vertical axis is often referred to as the Y axis, and the horizontal axis is referred to as the X axis.
The actual charted values, which are usually rows or columns of the source data.
The axis that represents the values or units of the source data.
The axis identifying each data series.
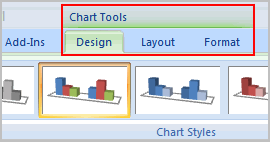
Once you insert a chart, a new set of Chart Tools, arranged into three tabs, will appear above the Ribbon. These are only visible when the chart is selected.
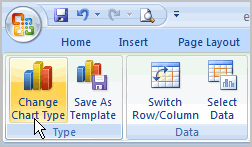
The chart in the example compares each salesperson's monthly sales to his or her other months' sales; however, you can change what is being compared. Just click the Switch Row/Column Data command, which will rotate the data displayed on the x and y axes. To return to the original view, click the Switch Row/Column command again.
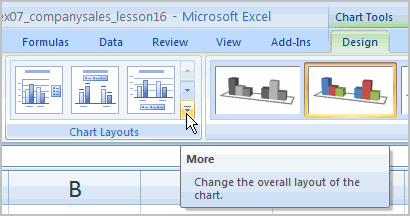
If your new layout includes chart titles, axes, or legend labels, just insert your cursor into the text and begin typing to add your own text.
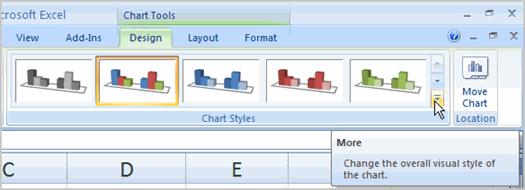
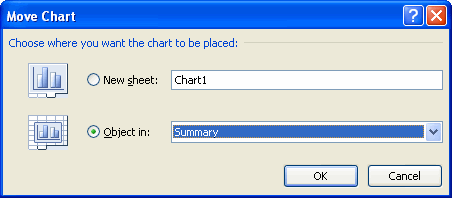
Use the Company Sales workbook or any other workbook to complete this challenge.
/en/excel2007/using-conditional-formatting/content/