Newton's Laws of Motion -
Newton's Third Law

Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Third Law


/en/newtons-laws-of-motion/newtons-second-law/content/
Newton's third law says that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction.
This means that whenever an object moves, pushes or presses another object, the second object reacts by returning the same amount of force.
Objects react by creating resistance, or pushing back. Here are some examples in which this law applies…
In order for rockets to reach space, they have to be propelled with great force. For this reason, their engines emit gasses downward, generating the needed thrust.
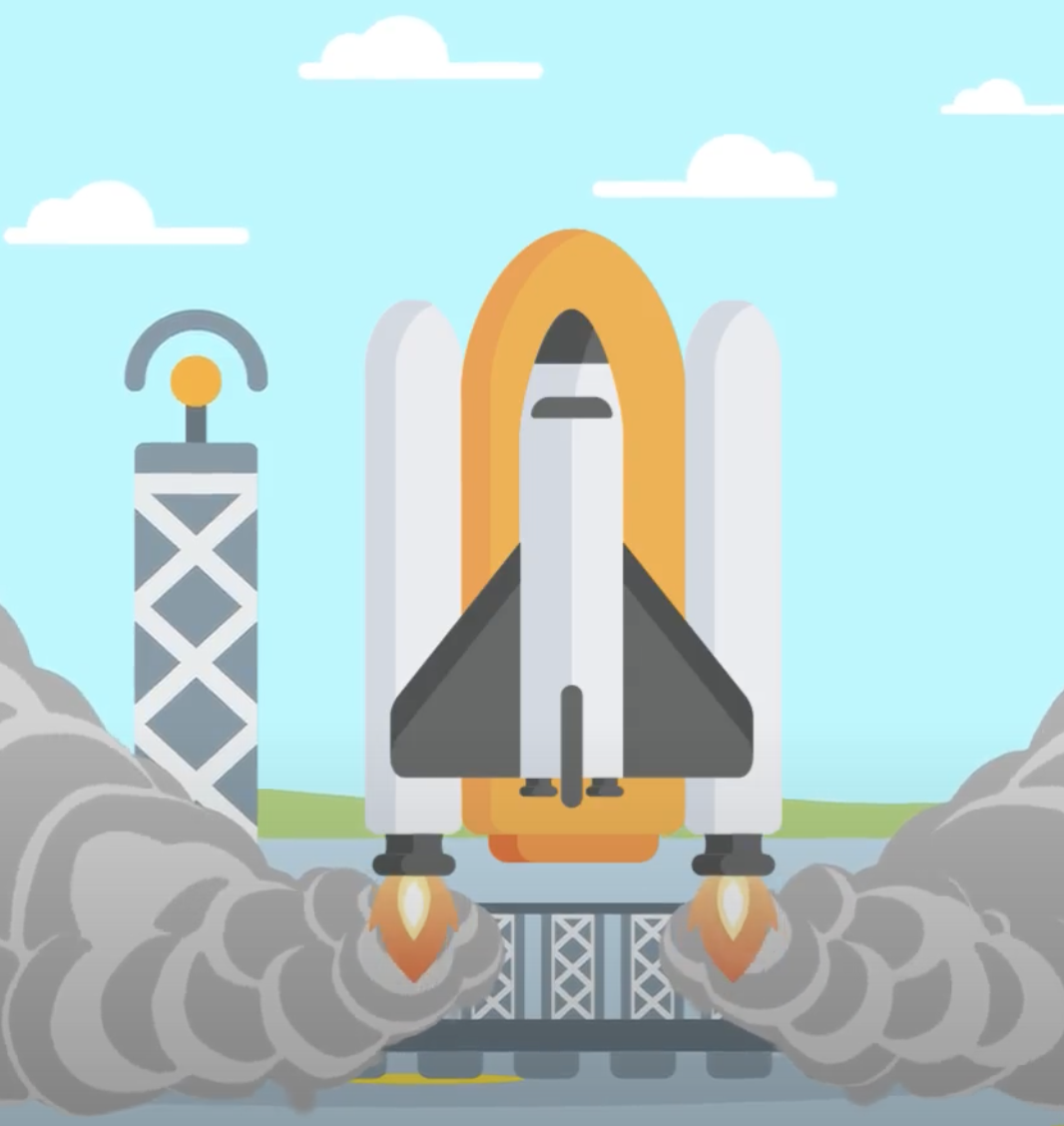

The expelled gas exerts a force on the rocket, following Newton's third law of motion—every action has an equal and opposite reaction. This leads to the rocket experiencing an upward force, which propels it into space. This upward motion is not caused by the ground pushing back; rather, it results from the force generated by the expulsion of gas.
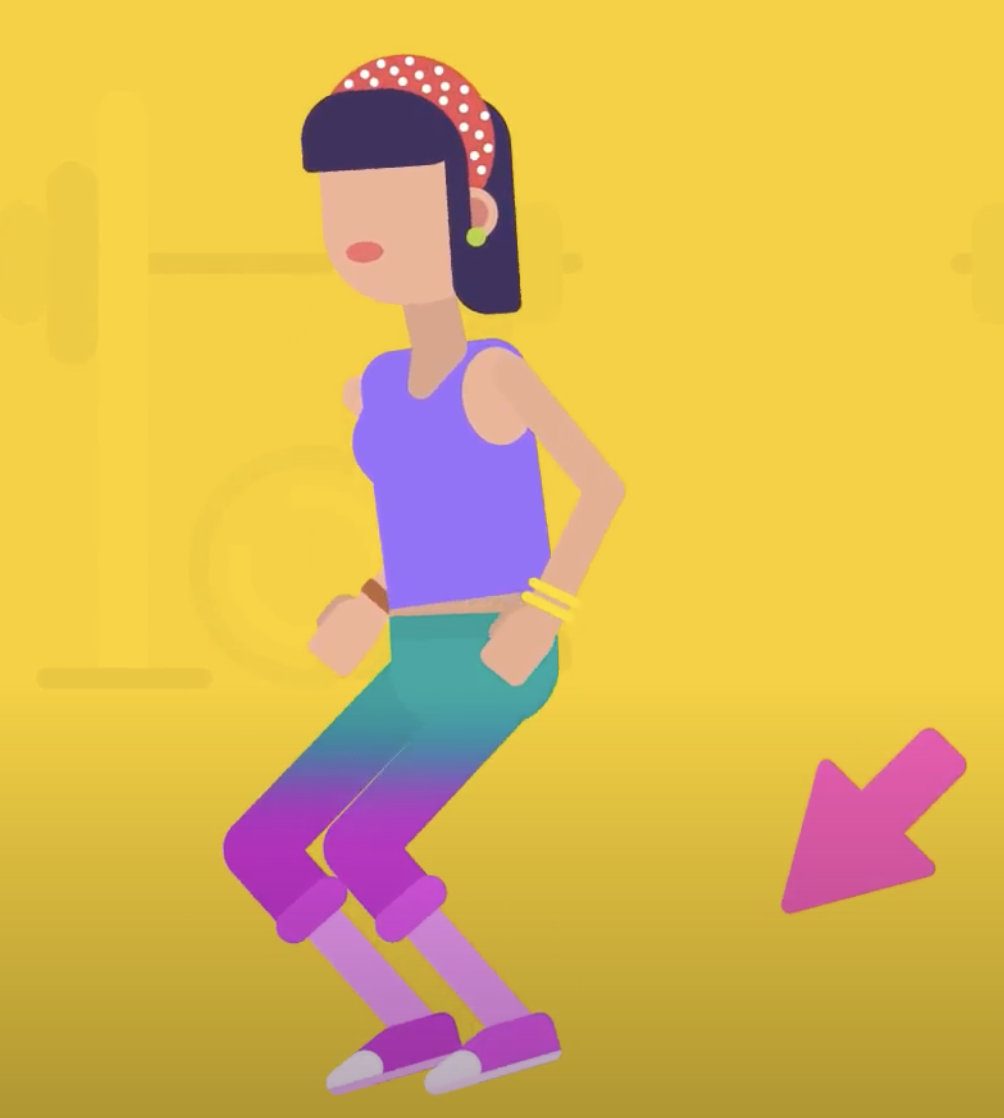
When a person jumps into the air, the force from their body is pushing downward, toward the ground. The ground pushes the person upward. If the person uses less force, they won’t jump as high.

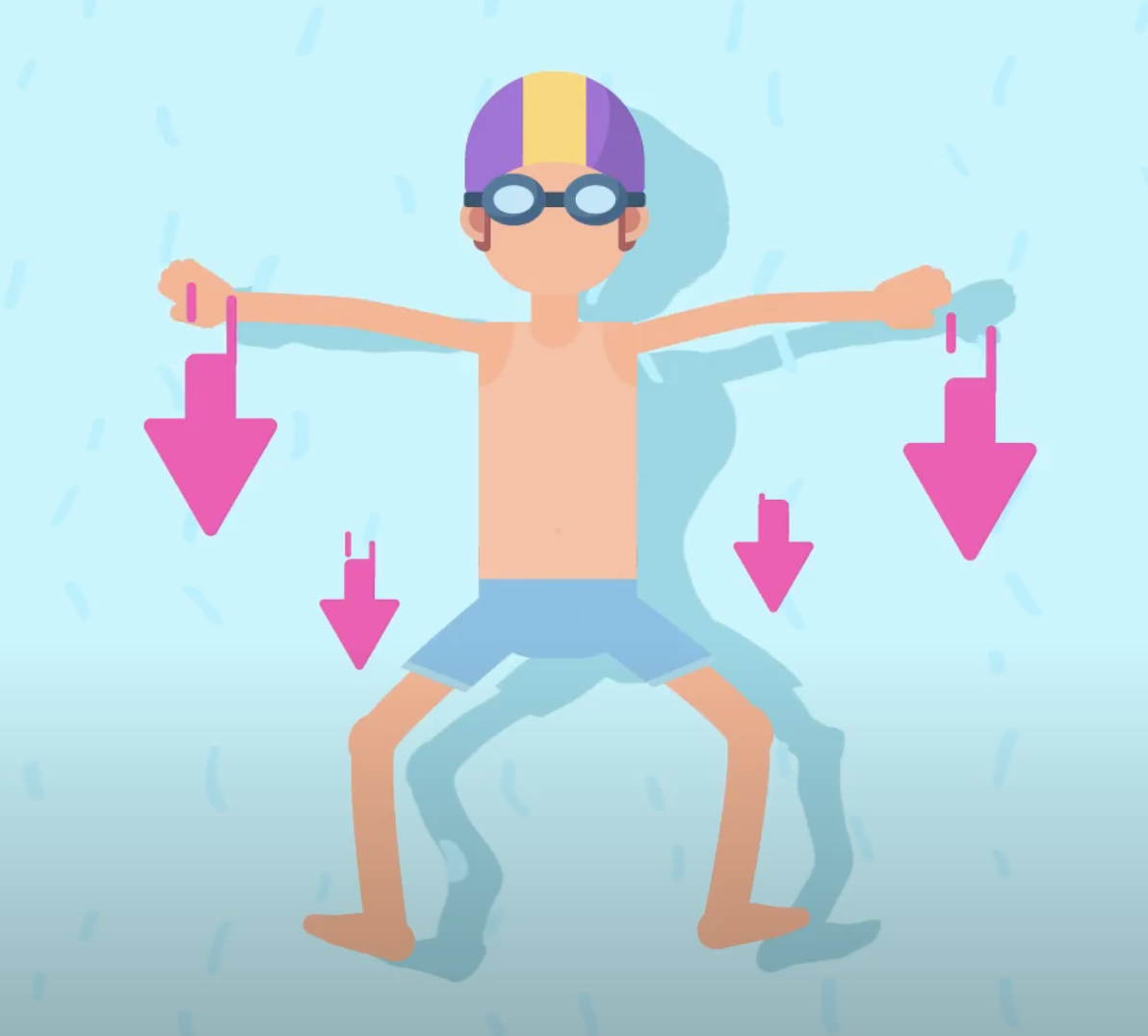
If you’re swimming in a pool and you push the water with your arms and legs, the water reacts by propelling you forward. The more force you use, the further and faster you’ll swim.

Hopefully this tutorial has helped you to understand Newton’s three laws of motion. Take the final quiz to see how much you learned!
/en/newtons-laws-of-motion/laws-of-motion-quiz/content/